24. Maintenance
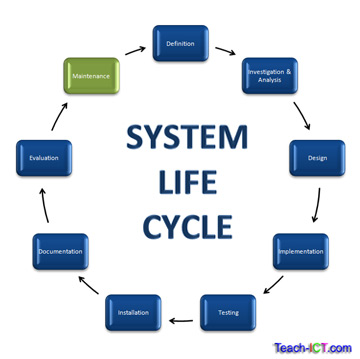 This phase continues for the lifetime of the system. The technical documentation is essential to support the maintenance stage.
This phase continues for the lifetime of the system. The technical documentation is essential to support the maintenance stage.
There are three kinds of maintenance needed:
- Corrective maintenance
- Adaptive maintenance
- Perfective maintenance
Corrective maintenance
This is where problems are identified with the system after installation. Perhaps an item on the template isn't printing out correctly or maybe one of the on-screen buttons isn't linking to the correct form.
A fault report is raised and the developers fix the problem. It is then passed over to a team of testers who check that the fault has been fixed. Once it has been passed by the testers, the fix will be released to the live system.
Corrective maintenance can also involve fixing hardware faults or replacing equipment as necessary.
Adaptive maintenance
This type of maintenance often occurs as a result of external influences or strategic changes within the company. For example, the Government recently changed the VAT rate from 17.5% to 20%. This change would have meant that many organisations had to make alterations to their systems. Perhaps a bank decides to offer a new mortgage product. This will have to be included in the system so that mortgage interest and payments can be calculated.
Perfective maintenance
The system has been in place and running fine for a while. However, over time, the end user will often find tweaks or minor improvements which could be made to improve the way the system works. Perhaps a slightly different screen or data input form. These tweaks are not major enough to prompt a complete new system, so the maintenance team adapt the system to suit.
It is important to be aware that while the system remains in use the maintenance stage will be ongoing.
challenge see if you can find out one extra fact on this topic that we haven't already told you
Click on this link: System maintenance
